October 11, 2024
Foot checkups for diabetics are crucial for preventing serious complications. Diabetes can lead to nerve damage and poor circulation, making feet vulnerable to infections and ulcers. Historically, many diabetics faced severe foot issues due to a lack of awareness about proper foot care. Regular foot checkups can catch problems early and save lives.
These checkups help identify blisters, calluses, or any signs of infection. They also educate patients on proper foot hygiene and footwear choices. By prioritizing foot health, diabetics can reduce the risk of amputations and enhance their quality of life. Don’t underestimate the importance of these checkups—your feet deserve the best care possible.
Key Takeaways
-
Regular foot checkups are crucial for diabetics to prevent serious complications. Schedule these exams at least once a year with a healthcare provider.
-
During foot exams, expect thorough assessments that check for circulation, sensation, and any abnormalities. Be prepared to discuss your daily foot care routine.
-
Always inspect your feet daily for any cuts, blisters, or changes in skin color. This early detection can help you address issues before they worsen.
-
Choose the right footwear that fits well and provides support. Avoid tight shoes or those that may cause friction on your feet.
-
Podiatrists play a vital role in managing diabetic foot health. Don't hesitate to consult them for specialized care and advice.
-
Educate yourself on the warning signs of foot problems, such as numbness or swelling, and seek help immediately if you notice any concerning symptoms.
Understanding Diabetic Foot Exams
Exam Components
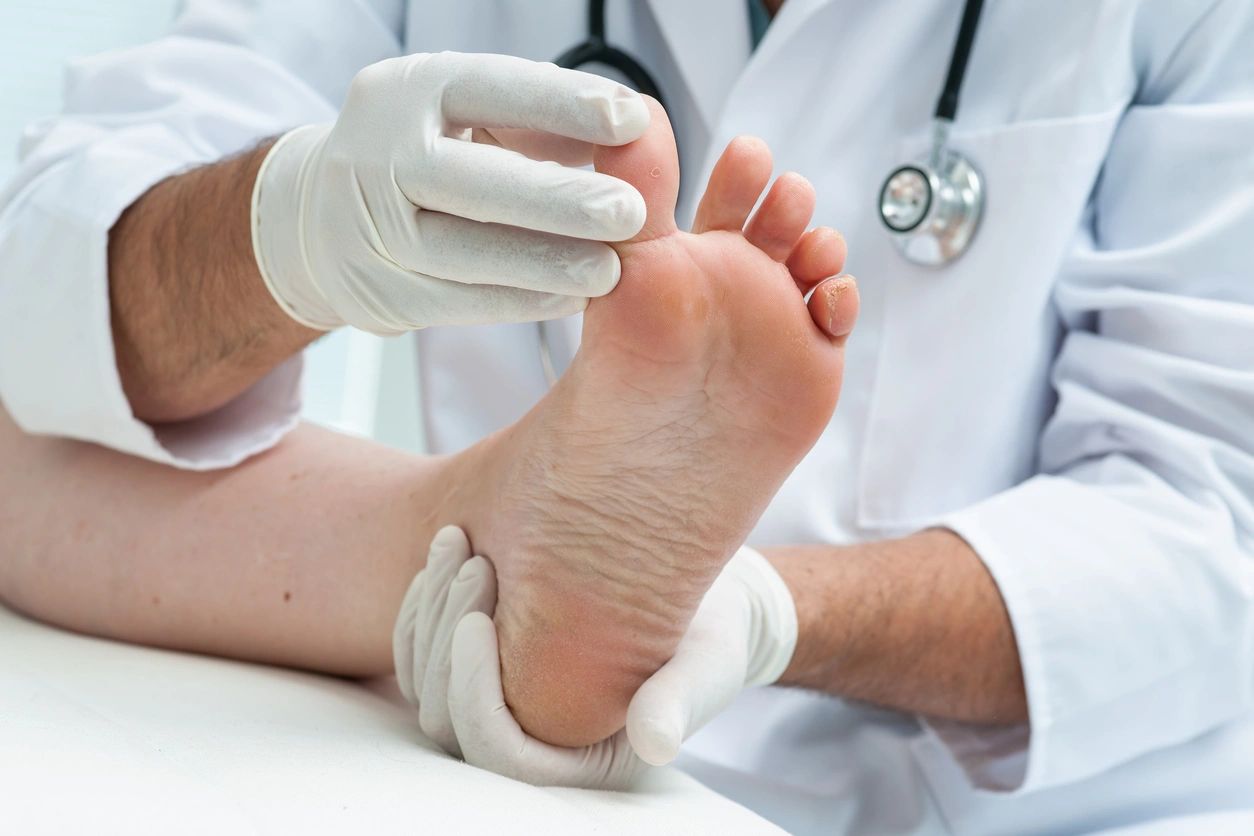
A diabetic foot exam is a thorough check-up of the feet for individuals with diabetes. It includes several key components. Healthcare providers assess foot structure and skin condition. They look for any signs of diabetic foot ulcerations or wounds. Sensation testing is also crucial. Providers use a monofilament or tuning fork to check for diabetic neuropathy. Regular exams help identify problems early.
Importance of Early Detection
Early detection of foot issues can prevent severe complications. Diabetes can lead to nerve damage and poor circulation. These conditions increase the risk of infections and ulcers. If left untreated, even minor injuries can escalate into serious issues. In fact, nearly 15% of diabetics develop foot ulcers at some point in their lives. This statistic highlights the need for regular screenings.
Role of Healthcare Professionals
Healthcare professionals play a vital role in conducting diabetic foot exams. They have specialized training to identify risks and complications. These professionals provide education on proper foot care and hygiene. They also guide patients on how to monitor their own feet at home. Regular visits to healthcare providers ensure that potential issues are caught early.
Importance of Regular Foot Checkups
Preventive Care
Consistent foot checkups are essential for diabetics. These exams help monitor potential issues before they become serious. Regular visits to a healthcare provider can identify early signs of foot problems. This proactive approach is vital in preventing complications.
Diabetes can lead to nerve damage and poor blood flow. This combination increases the risk of developing foot ulcers. If left untreated, these ulcers can lead to serious infections. In some cases, amputations may be necessary. Regular foot exams can catch these issues early and prevent them from worsening.
Serious Conditions
Foot care is crucial for diabetics. Poor foot care can lead to severe health risks. Regular checkups help detect conditions like calluses or blisters. These minor issues can escalate into serious foot problems if ignored.
Infections are a major concern for individuals with diabetes. A small cut or sore can quickly turn into a serious infection. According to the American Diabetes Association, nearly 200,000 amputations occur each year due to diabetes-related complications. Many of these cases could be prevented with proper foot care.
Blood Sugar Control
Blood sugar control directly affects foot health. High blood sugar levels can damage nerves and blood vessels. This damage reduces sensation in the feet and limits blood flow. As a result, injuries may go unnoticed and heal slowly.
Maintaining stable blood sugar levels is key to preventing foot issues. Regular checkups allow healthcare providers to assess both blood sugar control and foot condition. They can recommend changes in diet or medication if necessary.
Diabetics should also perform self-checks at home. Looking for redness, swelling, or sores is important. Early detection of any abnormalities can lead to prompt treatment.
Education and Awareness
Education about foot care is essential for diabetics. Understanding how diabetes affects the feet helps individuals take better care of them. Healthcare providers often give advice on proper footwear and hygiene practices.
Wearing well-fitting shoes can prevent many foot problems. Keeping feet clean and dry is also important in avoiding infections. Diabetics should avoid walking barefoot to reduce injury risk.
Regular foot checkups reinforce the importance of good habits. They provide an opportunity for patients to ask questions and learn more about their condition.
What to Expect During a Foot Exam

Complete Foot Exam
A complete foot exam is crucial for diabetics. It usually starts with a visual inspection. The foot doctor looks for any signs of foot symptoms, such as redness, swelling, or skin changes. This step helps identify potential issues early.
Next, the healthcare provider checks for any common foot wounds. They will assess areas where blisters or calluses may form. These can lead to more serious problems if not treated properly.
Nerve Function Tests
Tests for nerve function are essential during the foot exam. Healthcare providers often use a monofilament test. This test involves touching various parts of the foot with a thin filament. It helps assess sensitivity and detect neuropathy.
Another common test is the tuning fork test. The doctor places a vibrating tuning fork on the big toe. This checks for vibration sensation, which is vital for balance and mobility.
Skin Integrity Assessment
Assessing skin integrity is also important in a foot exam. The doctor examines the skin for dryness or cracking. These conditions can lead to infections if left untreated.
They may also check for foot ulcers or signs of foot infection. Early detection of these issues can prevent severe complications. Diabetics must pay attention to their feet since they are at higher risk for such problems.
Discussing Concerns
Patients should feel comfortable discussing any concerns with their healthcare provider during the exam. Questions about pain, numbness, or changes in appearance are all valid topics. Open communication helps doctors tailor their assessments effectively.
Discussing lifestyle factors is equally important. Factors like footwear choices and daily activities can impact foot health. Patients should share this information to receive personalized advice.
Follow-Up Care
After the initial assessment, follow-up care may be necessary. Regular visits help monitor any changes in foot health over time. This ongoing care is especially important for those with existing foot diseases or previous injuries.
Patients might receive recommendations for proper footwear and daily foot care routines. Adhering to these guidelines can significantly reduce the risk of severe complications.
In summary, understanding what to expect during a foot exam is vital for diabetics. A comprehensive evaluation includes visual inspections, nerve function tests, and skin assessments. Discussing concerns openly with healthcare providers enhances the effectiveness of these exams.
Foot Exam Results
Understanding Findings
Foot exams for diabetics reveal important information. Results can indicate the health of your feet. A thorough exam checks for skin integrity, circulation, and nerve function.
Normal results show no signs of ulcers or abnormalities. This indicates good foot health. However, abnormal results require attention. For example, severe foot ulcers may appear if there are issues with blood flow or nerve damage. These findings can lead to serious complications if not treated.
Common Results
Several common results arise from foot exams. Each result has specific implications for diabetic foot health.
-
Skin Changes: Dryness or cracking can signal potential problems.
-
Nerve Damage: Loss of sensation means you might not feel injuries.
-
Circulation Issues: Poor blood flow can lead to severe foot ulcers.
Severe foot ulcers are a major concern. They often develop from untreated minor injuries. In 2018, the American Diabetes Association reported that about 15% of diabetics experience foot ulcers at some point. This statistic highlights the importance of regular foot exams.
Seeking Further Evaluation
Not all exam results need immediate action. Some findings may require monitoring. Others, however, warrant further evaluation.
Consult a healthcare provider if you notice:
-
Persistent Pain: Unexplained pain in your feet could indicate issues.
-
Changes in Color: Blue or pale feet suggest poor circulation.
-
Infections: Redness, swelling, or discharge requires prompt attention.
Regular checkups help catch problems early. If an exam shows severe foot ulcers or other significant issues, seek care quickly. Early intervention can prevent complications like infections or amputations.
Educating yourself on how to interpret these results is crucial. Understanding what each finding means helps you take charge of your foot health.
Daily Foot Care Tips for Diabetics
Establish Routine
Diabetics should establish a daily foot care routine. This routine helps in maintaining foot health. Regular checks can prevent serious issues. Inspect feet every day for cuts, blisters, or redness. Use a mirror if needed to see the bottom of your feet.
Foot problems can arise from diabetes complications. Uncontrolled diabetes can lead to nerve damage. This makes it hard to feel injuries on the feet. Early detection is key to preventing diabetic foot ulcers.
Inspect Feet
Inspecting feet daily is crucial. Look for any changes in color or texture. Pay attention to swelling or new growths. These signs may indicate diabetic foot problems. If any issues arise, consult a healthcare provider immediately.
Use gentle soap and water to clean feet daily. Dry thoroughly, especially between toes. Moisturize feet to prevent dryness but avoid applying cream between toes. This area needs to stay dry to prevent fungal infections.
Moisturize Properly
Moisturizing is an important part of diabetic foot management. Keeping feet hydrated helps maintain skin integrity. Use a fragrance-free lotion that is suitable for sensitive skin. Apply lotion after washing and drying your feet.
Avoid soaking feet too long as it can lead to skin breakdown. Moisture balance is essential for healthy diabetes management. A good moisturizer prevents cracks and potential entry points for bacteria.
Document Changes
Documenting any changes in foot condition is vital. Keep a log of any issues noticed during inspections. Note down cuts, blisters, or changes in sensation. This information is useful when discussing with healthcare providers.
Regular communication with medical professionals is important for diabetic patients. They can provide tailored advice based on documented changes. This proactive approach supports effective diabetes self-management.
Seek Professional Help
Seek professional help when necessary. Schedule regular checkups with a podiatrist specializing in diabetic foot care. They can offer specialized insights into managing diabetic feet effectively.
Early intervention can prevent serious complications like diabetic foot ulcers. These ulcers are painful and may require extensive treatment if not addressed quickly.
Choosing the Right Footwear

Proper Fit
Selecting shoes that fit well is crucial for diabetics. Poorly fitting shoes can lead to foot problems like blisters, calluses, and ulcers. These issues can escalate quickly. They may result in serious complications, including infections. Diabetics often have reduced feeling in their feet due to nerve damage. This makes it harder to notice discomfort or pain. A proper fit helps prevent injuries that could lead to amputation.
Shoes should provide adequate support. Look for styles with a wide toe box. This allows toes to move freely without pressure. Shoes should also have cushioned insoles to absorb shock. Ensure that there is enough room for your foot to expand, especially during the day.
Avoiding High Heels
High heels and tight footwear are not suitable for diabetics. They can cause foot complications by putting excessive pressure on certain areas of the foot. This increases the risk of developing ulcers or other injuries. Tight shoes restrict blood flow, which is critical for healing injuries.
Instead, opt for low-heeled shoes with a stable base. These types of shoes help maintain balance and reduce the risk of falling. Comfort should always be a priority when choosing footwear.
Features to Consider
Look for diabetic-friendly socks and shoes with specific features. Socks should be made from moisture-wicking materials. This keeps feet dry and prevents fungal infections. Avoid socks with seams that could rub against the skin.
Shoes should have a soft lining to minimize friction. Consider those with adjustable straps or laces for a customized fit. Some diabetic shoes come with extra depth, allowing for custom orthotics if needed.
Here are key features to look for in diabetic footwear:
-
Cushioning: Provides comfort and absorbs impact.
-
Breathability: Helps keep feet cool and dry.
-
Stability: Supports the foot's structure during movement.
-
Adjustability: Allows for a personalized fit.
Regular Checkups
Regular foot checkups are essential for people with diabetes. They help identify any potential issues early on. Early detection can prevent serious complications like gangrene or severe infections.
Foot care does not end with choosing the right footwear. It is vital to inspect your feet daily for any signs of problems such as redness or swelling. Keeping track of your foot health will help you stay proactive.
Recognizing Warning Signs Early
Key Symptoms
Swelling or discoloration in the feet can indicate serious issues for diabetics. Redness, warmth, or a change in skin texture may also signal a problem. These symptoms can lead to serious infections if not addressed quickly.
Numbness or tingling sensations are other warning signs. They may suggest nerve damage, which is common among diabetics. If these feelings persist, it is crucial to consult a healthcare provider.
Pain in the feet should never be ignored. It can indicate various problems, including blood vessel damage or infections. Early identification of these symptoms helps prevent further complications.
Importance of Vigilance
Being vigilant about foot health is essential for diabetics. Regular checkups can help identify potential risks early. This proactive approach can prevent severe complications down the line.
Changes in foot condition may occur without noticeable pain. Thus, routine self-assessments are vital. Look for cuts, blisters, or any signs of infection regularly. Even small wounds can become significant issues if left untreated.
Diabetics often have reduced blood flow to their extremities. This makes it harder for wounds to heal and increases the risk of infection. Therefore, monitoring foot health must be part of daily care routines.
Regular Self-Assessment
Self-assessment is an effective way to catch problems early. Diabetics should inspect their feet daily for any changes. Use a mirror to check hard-to-see areas like the soles and between toes.
Keeping track of foot conditions helps create a clearer picture of overall health. Any changes should prompt immediate medical attention from a doctor or primary care provider.
Establishing a routine for foot checks can be beneficial. Set aside a few minutes each day for this task. It takes little time but can save significant trouble later on.
Treatment Options
If any issues arise, treatment options vary based on the problem's severity. Minor cuts may need cleaning and dressing, while more severe infections might require antibiotics or even surgery.
Consulting with healthcare providers ensures proper treatment plans are in place. They can guide patients on managing symptoms and preventing future issues effectively.
Role of Podiatrists in Diabetes Care
Specialized Training
Podiatrists receive extensive training in foot health. They complete a Doctor of Podiatric Medicine (DPM) degree, which typically requires four years of study after obtaining a bachelor’s degree. Their education includes specialized courses on diabetes treatment and foot disorders.
Podiatrists learn to recognize complications that arise from diabetes. They understand how high blood sugar affects the feet. This knowledge is crucial for preventing serious issues like infections or amputations. Many podiatrists also pursue additional training in diabetic foot care, enhancing their skills further.
Tailored Treatment Plans
Podiatrists create personalized treatment plans for patients with diabetes. Each plan addresses specific needs based on individual health conditions. For example, they assess foot structure, circulation, and sensation. This assessment helps them identify potential problems early.
Treatment may include custom orthotics to improve foot alignment. These devices help distribute pressure evenly across the foot, reducing the risk of ulcers. Podiatrists also provide wound care for existing injuries. They teach patients how to properly care for their feet at home.
Regular checkups are vital for effective management of diabetic foot health. These appointments allow podiatrists to monitor changes over time. Early intervention can prevent more severe complications from developing.
Collaborative Approach
Collaboration between podiatrists and primary care providers is essential for comprehensive diabetes management. This teamwork ensures that all aspects of a patient’s health are addressed. Primary care providers often refer patients to podiatrists for specialized care.
Communication between healthcare professionals improves outcomes. Podiatrists share findings with primary care providers during consultations. This exchange of information allows for coordinated treatment plans tailored to each patient’s needs.
Patients benefit from this integrated approach. It ensures they receive holistic care that includes monitoring blood sugar levels and managing foot health simultaneously.
In summary, podiatrists play a crucial role in diabetes care through their specialized training and tailored treatment plans. Their collaborative efforts with primary care providers enhance overall diabetes management, leading to better health outcomes for patients.
Final Thoughts
Regular foot checkups are crucial for diabetics. They help catch issues early, preventing serious complications. Understanding what to expect during these exams empowers you to take charge of your health. Daily foot care and choosing the right footwear can significantly improve your quality of life.
Don’t wait for problems to arise. Schedule your foot exam today and stay proactive about your health. Your feet deserve the best care, and with the right knowledge, you can make informed decisions. Trust in the expertise of podiatrists and prioritize your foot health. Take action now for a healthier tomorrow!
Frequently Asked Questions
What is a diabetic foot exam?
A diabetic foot exam is a thorough evaluation of the feet to check for complications like neuropathy, ulcers, and infections. Regular exams help prevent serious issues.
How often should diabetics have foot checkups?
Diabetics should have foot checkups at least once a year. More frequent visits may be necessary for those with existing foot problems or high risk.
What happens during a diabetic foot exam?
During the exam, a podiatrist checks for skin changes, circulation issues, and nerve damage. They may also assess your footwear and provide care recommendations.
Why are regular foot checkups important for diabetics?
Regular checkups help catch problems early, reducing the risk of severe complications like infections or amputations. Prevention is key to maintaining foot health.
What daily foot care tips should diabetics follow?
Diabetics should wash feet daily, dry them thoroughly, moisturize (but avoid between toes), inspect for cuts or blisters, and trim nails carefully.
How can I choose the right footwear as a diabetic?
Select shoes that fit well, provide support, and have cushioning. Avoid tight-fitting styles and opt for breathable materials to prevent moisture buildup.
What warning signs should diabetics watch for in their feet?
Look out for redness, swelling, blisters, wounds that don’t heal, or any changes in color or temperature. Early detection can prevent serious complications.
Not what you were looking for? Step Ahead Podiatry also offers the following:
Foot surgery
Orthotics
Bunion Treatment
Step Ahead Podiatry’s Top Resources on Foot Pain:
Mayo Clinic on Foot Pain
American Podiatric Medical Association (APMA) on Foot Health
WebMD on Foot Problems